Oil coolers are tube heat exchangers that are specifically designed for the transfer of heat, or thermal energy, from heated oil by carrying the oil through cooling units in order to cool it, or using the oil to absorb heat. It can be used to cool items 100°C or higher; unlike water, which has a much lower boiling point. Particularly useful for automotive or mechanical applications, oil is an electrical insulator that is used inside of or in direct contact with electrical components. Read More…
Enerquip is your trusted shell and tube heat exchanger partner. Our in-house, thermal design engineers and ASME welders and fabricators can design and build custom engineered solutions for your company’s specific needs. Our experience and expertise have earned us a preferred supplier status with leading companies in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, cannabis, personal care, chemical,...
At Harris Thermal Transfer Products, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge heat exchangers designed to meet the diverse needs of our clients. We excel in producing a wide range of thermal management solutions, from standard models to highly customized systems. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures that our heat exchangers provide superior performance, reliability, and efficiency.

Since 1947, Perry Products Corporation has been a trusted designer, manufacturer and long term heat exchanger partner for our customers. In addition to custom thermal engineered shell and tube heat exchangers, Perry maintains a line of partially fabricated but still customizable ASME heat exchangers in stock and ready to ship quick. Direct and honest communication and on time delivery is one of...

At Ward Vessel and Exchanger, we take pride in designing and manufacturing heat exchangers and pressure vessels that reflect the depth of our engineering experience and our dedication to long-term performance. We approach every project with a commitment to understanding our customers’ thermal and mechanical requirements, allowing us to create custom heat exchanger solutions that maximize...

Doucette Industries has been a leader in suction line heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, marine heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers and tube-in-tube water cooled condensers since 1975. We offer full customization services, and experienced staff, rapid response to your inquiries and a wide selection of cutting edge products. Please visit our website for more information.
At West Warwick Welding, we bring together decades of fabrication experience and a commitment to precision workmanship to support customers who rely on durable, high-performance heat exchanger solutions. We operate as a fully integrated welding and fabrication shop, and we take pride in managing every stage of production with the same level of care, from the initial design consultation to the...
More Oil Cooler Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Oil Coolers: Applications, Types, and Benefits
Oil coolers play a vital role in modern machinery by maintaining optimal operating temperatures for a wide array of industrial and commercial equipment. These essential heat exchangers are engineered to dissipate excess heat from lubricating oils, hydraulic fluids, transmission oils, and compressor oils, ensuring efficient system performance, minimizing wear and tear, and extending the lifespan of critical components.
Key Applications of Oil Coolers Across Industries
Oil coolers find widespread use in numerous sectors due to their ability to stabilize fluid temperatures and prevent overheating. Common applications for oil coolers include:
- Torque Converters: Managing heat generated during power transmission in automotive and heavy equipment.
- Hydraulic Systems: Cooling hydraulic oil in presses, injection molding machines, and construction machinery to optimize hydraulic circuit efficiency.
- Transmission Oil Cooling: Maintaining stable transmission fluid temperatures in vehicles, especially trucks, buses, and off-highway equipment.
- Engine Oil Cooling: Essential for high-performance and heavy-duty engines in vehicles used for industrial towing, construction, agriculture, marine vessels, and military applications.
- Compressor Oil Cooling: Ensuring reliable operation of air compressors and refrigeration units by preventing thermal breakdown of compressor lubricants.
- Waste Heat Recovery: Capturing and repurposing heat energy from process oils to improve overall energy efficiency.
- Other Fluids: Cooling lubricating oils, transformer oils, quenching oils, and specialty fluids in chemical processing and electronics manufacturing.
Industries leveraging oil cooler technology include automotive, aerospace, marine, construction, mining, manufacturing, chemical processing, commercial HVAC, electronics, and power generation. For each sector, maintaining the appropriate oil temperature is crucial for maximizing machinery performance, minimizing downtime, and protecting valuable equipment investments.
Why Oil Temperature Control Matters: Performance and Reliability
Engine and machinery oils serve dual functions: they lubricate moving parts and dissipate excess heat. If the oil overheats, several critical problems can arise:
- Decreased Lubricating Properties: High temperatures can cause oil viscosity to drop, reducing its ability to form a protective film between moving parts.
- Thermal Degradation: Overheated oil oxidizes and breaks down, generating sludge, varnish, and acid that can corrode engine components.
- Reduced Horsepower: Excessive oil heat can lead to power loss and diminished engine efficiency.
- Potential Engine Seizure or Failure: If oil can no longer lubricate effectively, it can result in catastrophic engine damage or total system failure.
By incorporating a high-quality oil cooler into your system, you can:
- Maintain optimal oil temperature ranges for peak performance.
- Extend oil life and reduce maintenance intervals.
- Increase equipment reliability and uptime.
- Lower total cost of ownership by minimizing repairs and part replacements.
Are you wondering how to select the right oil cooler for your application? Jump to our selection guide below.
Types of Oil Coolers: Hydraulic Oil Coolers vs. Oil Air Coolers
Oil coolers are available in various designs, each tailored to specific use cases and operating environments. The two primary categories of oil cooling systems are hydraulic oil coolers and oil air coolers:
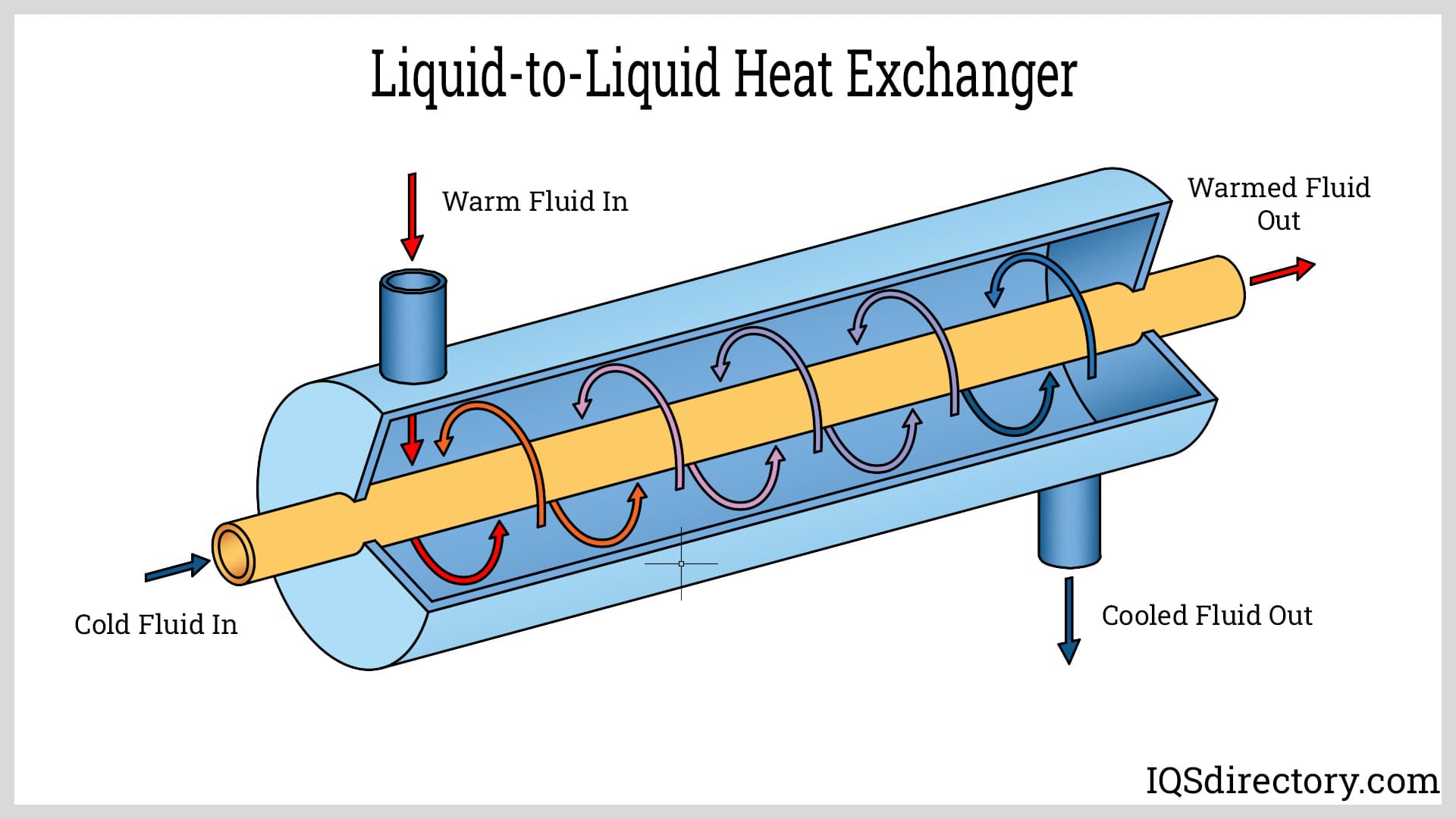
Hydraulic Oil Coolers (Water-to-Oil Coolers)
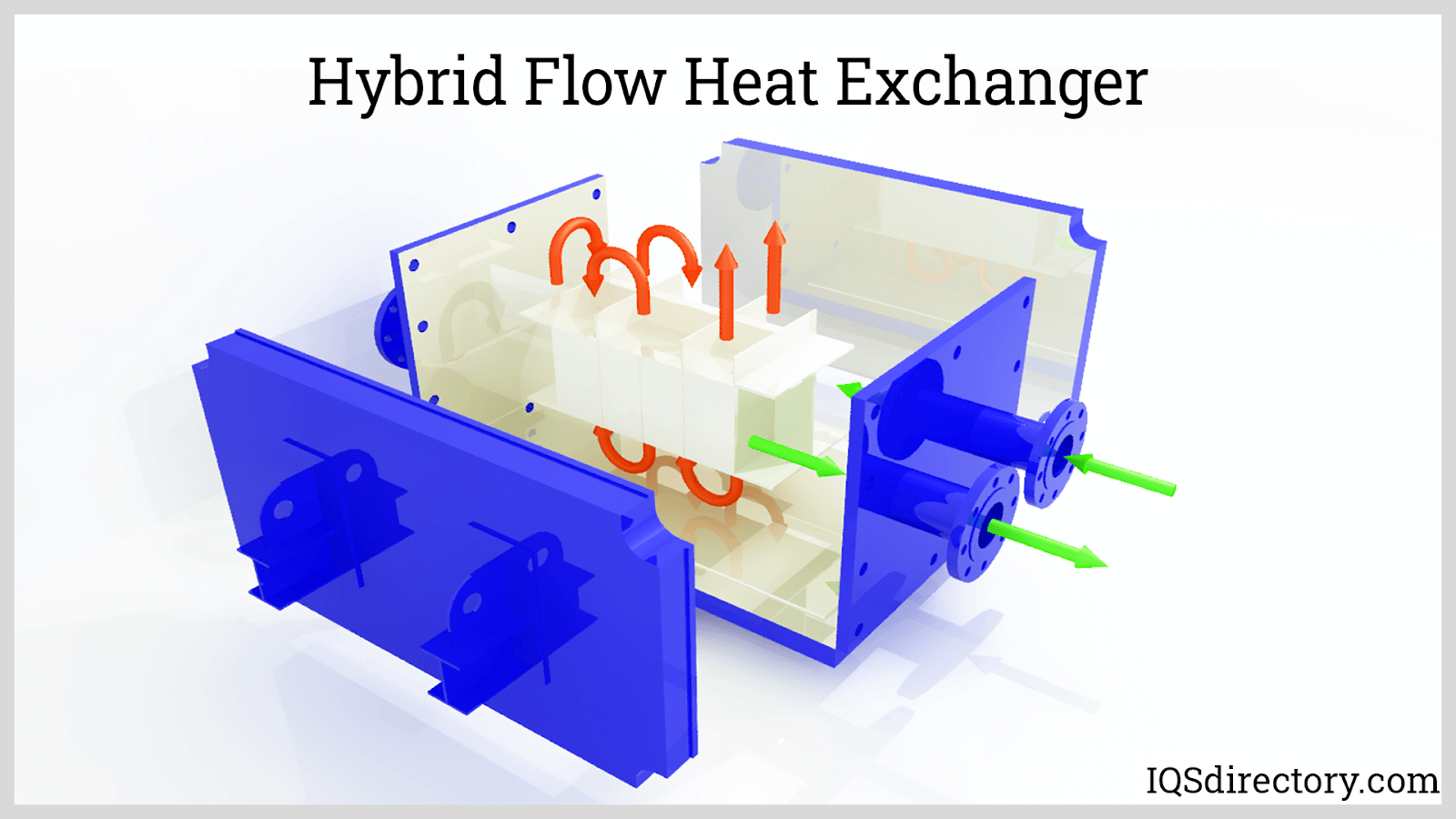
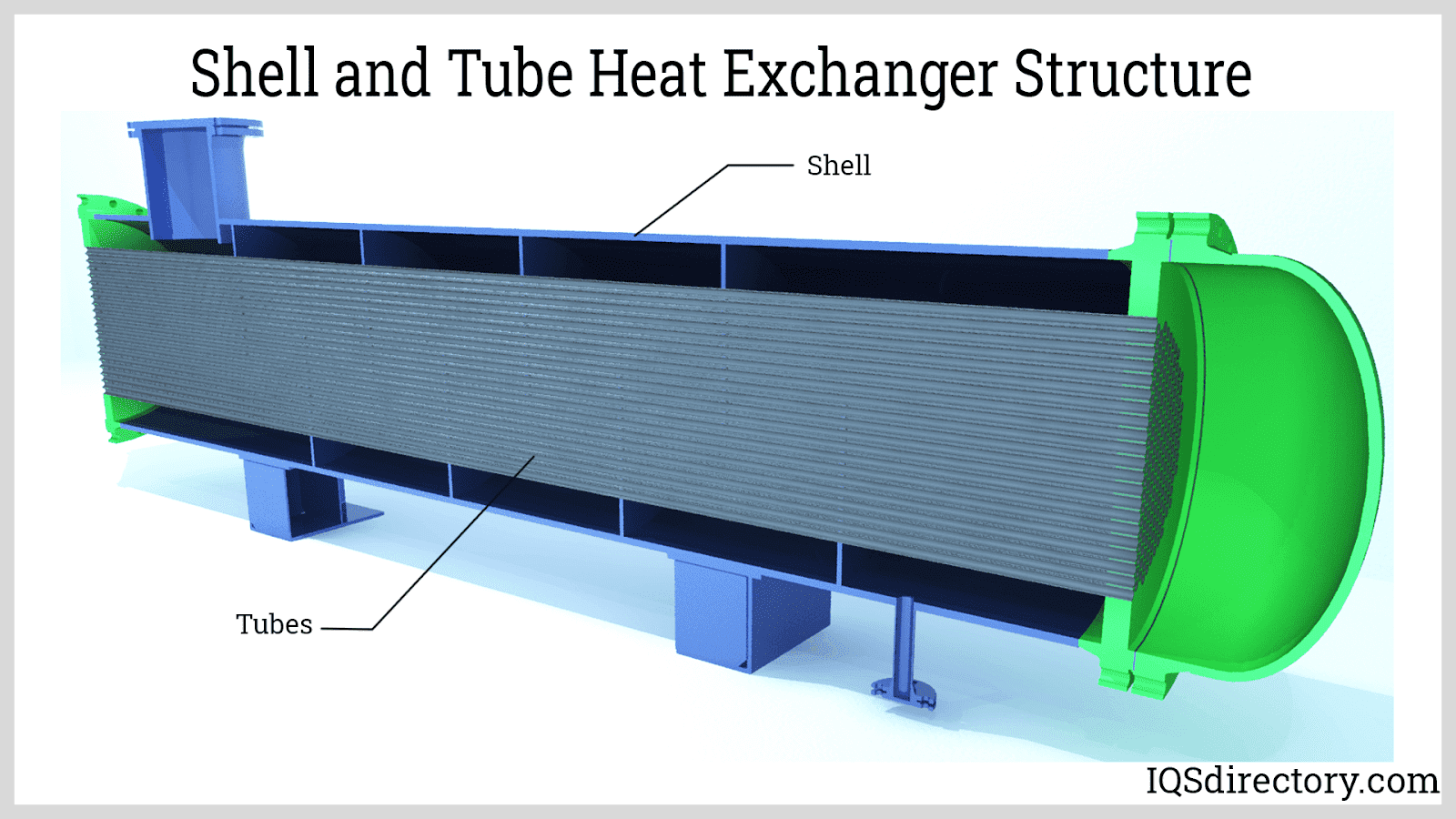
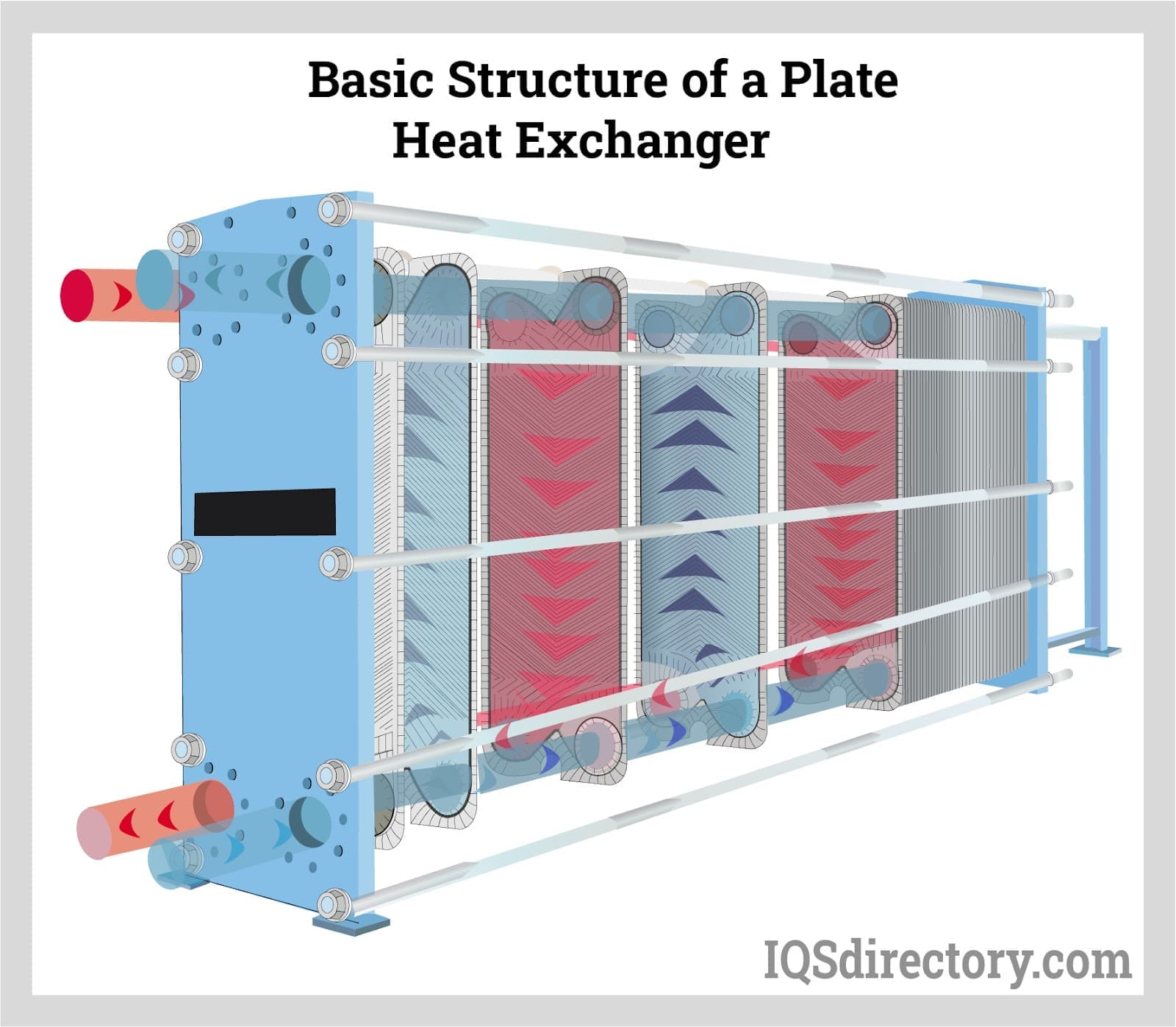
Hydraulic oil coolers, often called shell and tube or plate heat exchangers, use a liquid coolant (typically water or a water/glycol mixture) to absorb and carry away heat from hot oil. Their design features metal partitions—such as tubes or plates—through which the fluids flow on opposite sides. Key advantages and applications include:
- Efficient Heat Transfer: The large surface area of the plates or tubes enables rapid and efficient heat dissipation.
- High Capacity: Ideal for high-power hydraulic systems and continuous-duty industrial machinery.
- Stable Temperature Control: Well-suited for environments where precise oil temperature regulation is required.
- Versatility: Commonly found in injection molding, metalworking, power plants, marine propulsion systems, and heavy construction equipment.
Hydraulic oil coolers are also used for transformer oil cooling, quenching oil cooling, and in systems where water is plentiful and recirculation is possible.
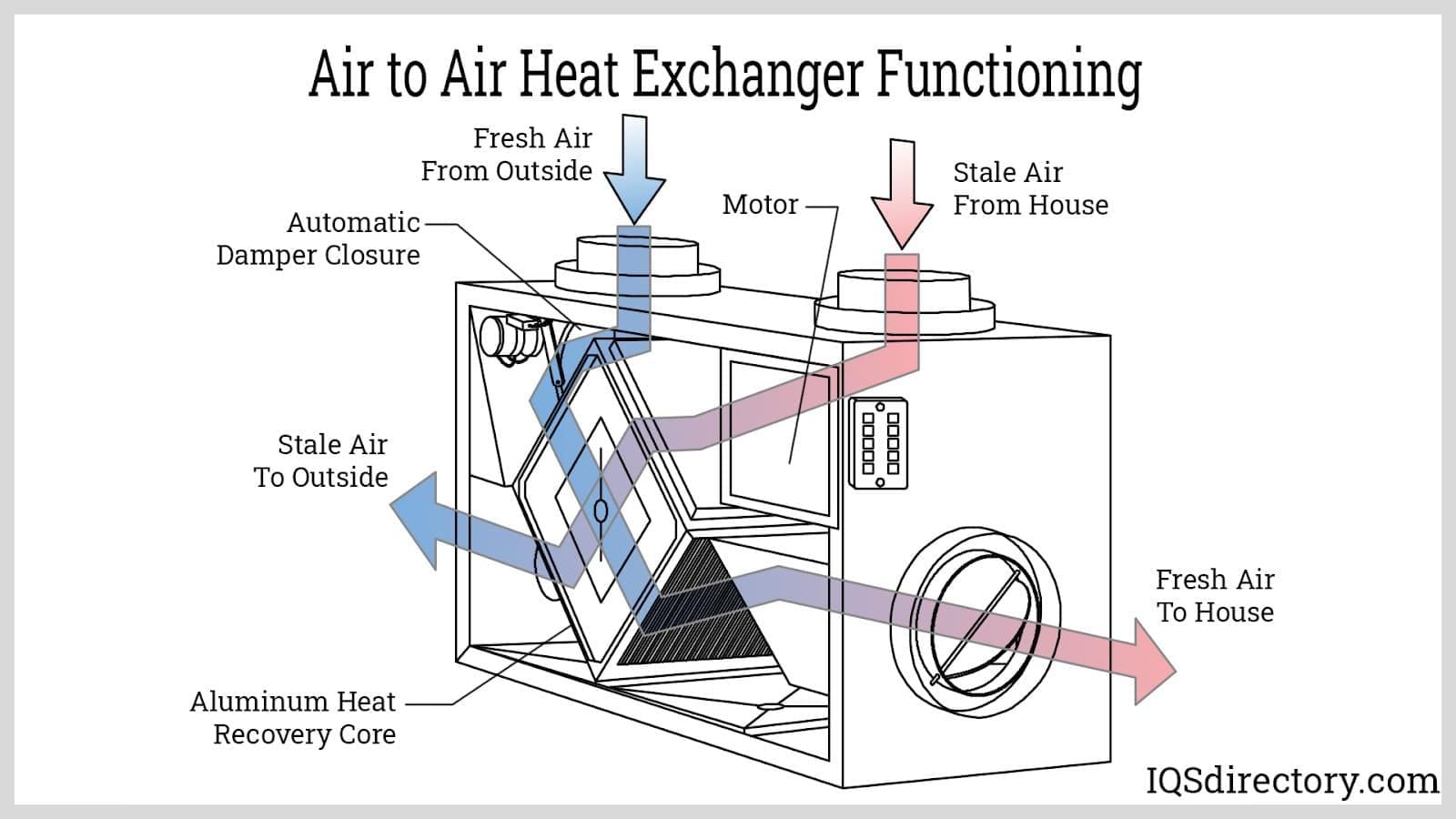
Oil Air Coolers (Air-to-Oil Coolers)
Oil air coolers use ambient air as the cooling medium. In these systems, hot oil flows through a series of thin, corrugated metal plates, while air is forced across the surface—typically using a fan. Heat transfers from the oil to the air, which is then expelled into the environment. Notable benefits and use cases include:
- Compact and Lightweight: Oil air coolers require less installation space and are easier to integrate into mobile or space-constrained equipment.
- Energy Efficient: They operate without the need for external water sources or pumps, reducing utility costs and maintenance complexity.
- Ideal for Remote or Mobile Applications: Frequently used in agricultural machinery, construction vehicles, mining equipment, and portable compressors.
- Low Maintenance: No need for water treatment or risk of coolant leaks.
Oil air coolers are available in plate, plate-and-frame, and flat plate configurations. They are suitable for a wide range of industrial, automotive, and commercial HVAC oil cooling needs.
How Do Oil Coolers Work? Understanding the Heat Exchange Process
Oil coolers operate based on the principles of heat exchange. The process involves transferring thermal energy from the hot oil to a cooler medium (air or liquid), thereby lowering the oil’s temperature without mixing the fluids. Here’s how the process works for each type:
- Hydraulic Oil Coolers: Hot oil circulates on one side of a metal barrier while the coolant flows on the opposite side. The heat from the oil is conducted through the metal wall and absorbed by the coolant, which is then carried away and dissipated.
- Oil Air Coolers: Heated oil passes through a network of thin plates or tubes. Air, either ambient or forced by a fan, moves across the exterior surfaces, pulling heat away from the oil and releasing it into the atmosphere.
The efficiency of an oil cooler depends on factors such as the surface area of the heat exchange plates, the flow rates of the fluids, temperature differentials, and the thermal conductivity of the materials used. For maximum performance, it is essential to size the oil cooler correctly for your application’s heat load.
Benefits of Oil Coolers: Why Invest in Quality Oil Cooling Solutions?
Integrating an oil cooler into your machinery or vehicle delivers a range of operational and financial advantages. Key benefits include:
- Extended Equipment Life: Prevents premature wear and component failure by maintaining safe oil temperatures.
- Improved System Efficiency: Keeps lubricants within optimal viscosity ranges, reducing friction and energy losses.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Minimizes the formation of sludge, varnish, and carbon deposits that can clog systems and increase service frequency.
- Enhanced Safety and Reliability: Limits the risk of unexpected breakdowns, downtime, and safety incidents caused by overheated oils.
- Optimized Performance: Supports consistent, high-power output from engines, transmissions, and hydraulic systems.
- Energy and Cost Savings: Improves overall system energy efficiency and lowers long-term operating expenses.
Curious about how oil coolers can improve your specific application? Contact our technical team for expert consultation and custom solutions.
How to Select the Right Oil Cooler: Key Decision Factors
Choosing the optimal oil cooler for your system involves evaluating multiple performance criteria and application requirements. Key factors to consider include:
- Heat Load: Calculate the amount of heat that needs to be removed from the oil based on system power, duty cycle, and ambient conditions.
- Fluid Compatibility: Ensure the cooler materials are compatible with the type of oil or fluid in use (hydraulic oil, engine oil, synthetic lubricants, etc.).
- Installation Space: Assess available mounting space, weight restrictions, and orientation limitations.
- Cooling Medium: Determine whether you have access to water (for hydraulic coolers) or must rely on ambient air (for oil air coolers).
- Operating Environment: Consider exposure to harsh weather, dirt, vibration, and corrosive agents.
- Maintenance Requirements: Evaluate ease of access for cleaning, servicing, and replacement.
- Regulatory Compliance: Check for industry or location-specific standards regarding safety, emissions, and environmental impact.
- Budget and Lifecycle Costs: Factor in initial investment, energy consumption, maintenance, and expected service life.
For help sizing and specifying an oil cooler for your application, explore our Oil Cooler Sizing Guide or request a quote from our engineering team.
Industry-Specific Applications and Use Cases
Automotive and Motorsports
Oil coolers are critical in high-performance vehicles, race cars, and commercial fleets. They manage thermal loads in engine oil, automatic transmission fluid, and differential oil, ensuring stable performance during prolonged high-speed driving, towing, or heavy haulage. Upgrading to a premium automotive oil cooler can significantly extend engine life and improve fuel efficiency.
Industrial Hydraulic Systems
In manufacturing plants, oil coolers protect hydraulic circuits from overheating during continuous operation. Applications include injection molding, stamping presses, CNC machines, and robotics. A properly engineered hydraulic oil cooler helps prevent system downtime and supports tighter process control.
Construction and Heavy Equipment
Excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes generate substantial heat in their hydraulic and transmission systems. Oil air coolers provide reliable, low-maintenance thermal management for mobile and off-highway equipment operating in rugged, remote environments.
Marine and Offshore
Marine engines, gearboxes, and hydraulic winches require robust oil cooling to withstand high loads and saltwater exposure. Marine-grade oil coolers are built with corrosion-resistant materials and compact designs for use in ships, boats, drilling platforms, and offshore wind turbines.
Chemical and Power Generation
Oil coolers are essential in chemical processing plants for cooling transformer oil, compressor oil, and process lubricants. Power plants use oil coolers for turbine lubrication systems and waste heat recovery, improving overall plant efficiency and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions About Oil Coolers
What size oil cooler do I need?
The size of oil cooler required depends on your system's heat load, flow rates, and installation constraints. Use our Oil Cooler Sizing Guide or consult our technical experts for a tailored recommendation.
How do I maintain my oil cooler?
Routine maintenance includes checking for leaks, cleaning debris from air or water passages, and inspecting for corrosion or mechanical damage. Schedule regular oil analysis to monitor for contamination and thermal degradation.
Can oil coolers be retrofitted to existing systems?
Yes, many oil cooler models are designed for retrofit applications. Ensure compatibility with your system’s oil type, flow rates, and available space. Our retrofit oil cooler solutions can help you upgrade for better performance.
What are signs that my oil cooler needs replacement?
Indicators include rising oil temperatures, reduced system efficiency, visible leaks, excessive pressure drop, or evidence of internal contamination. If you notice these symptoms, schedule an inspection or contact us for troubleshooting support.
Get Expert Help: Optimize Your Oil Cooling System
Choosing the right oil cooler is critical to maximizing equipment uptime, minimizing maintenance costs, and ensuring long-term reliability. Whether you need a compact air-to-oil cooler for mobile equipment or a high-capacity water-to-oil heat exchanger for industrial use, our team can assist you at every step—from sizing and selection to installation and after-sales support.
Ready to improve your system’s thermal management? Contact us today for expert guidance and discover how the right oil cooler can enhance your equipment’s performance, reliability, and efficiency.











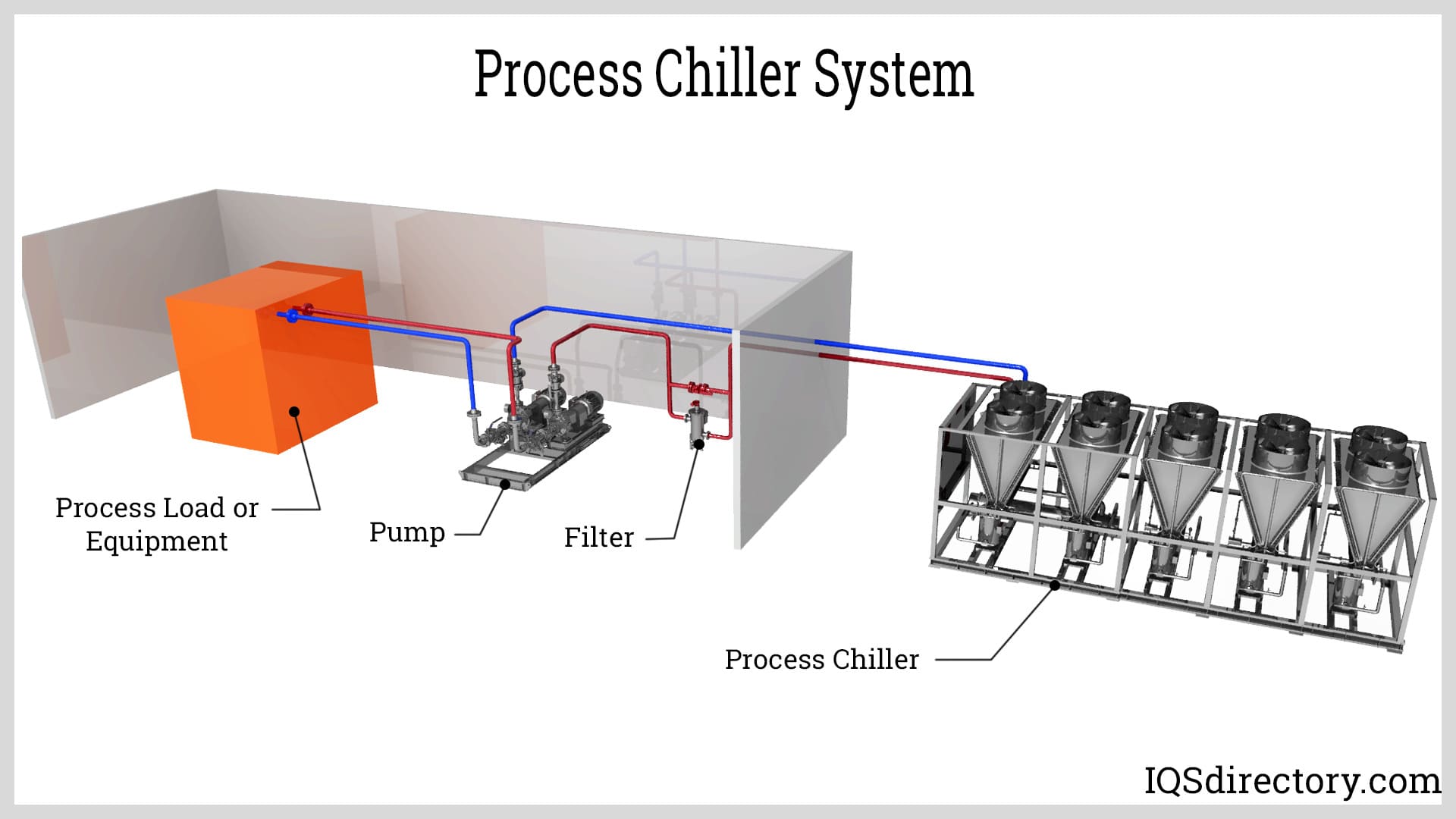
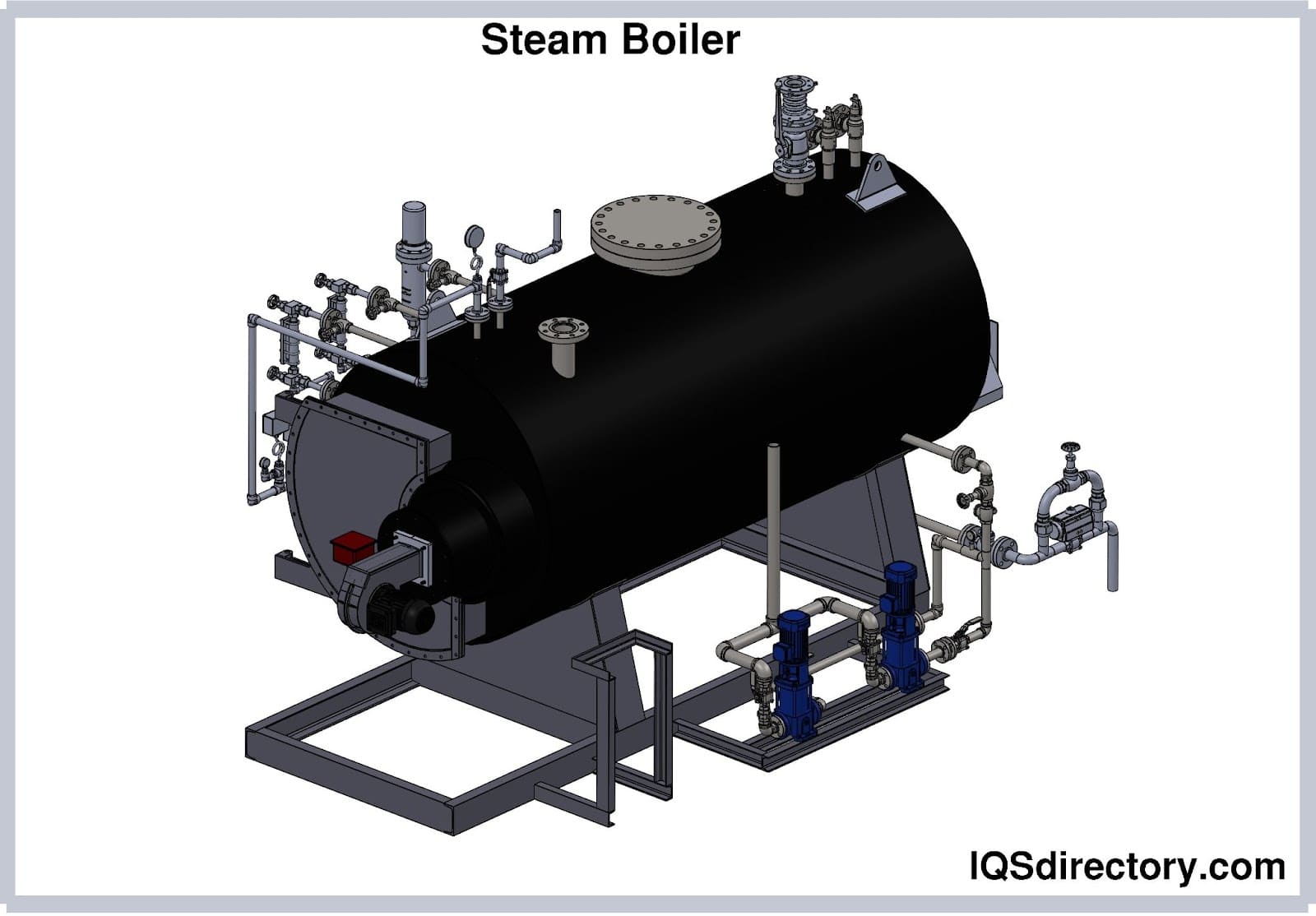
 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services